Beginner bodyweight workoutsleverage your own body mass as natural resistance, eliminating the need for gym equipment. These functional exercises incorporate fundamental movement patterns like push-ups for upper body strength, bodyweight squats for lower body development, core-stabilizing planks, and balance-enhancing lunges—all targeting primary muscle groups while enhancing postural alignment and trunk stability.
The versatility of calisthenics allows for training in any environment, from home spaces to outdoor settings, with scalable progressions suitable for novice to intermediate fitness enthusiasts. Consistent training produces tangible results within a 4-week period, including significant strength development, enhanced muscular endurance, improved joint mobility, and better movement efficiency.
This accessible approach to functional fitness creates a sustainable foundation for long-term physical development and movement competency through these evidence-based, adaptable exercises.
- Bodyweight training utilizes your own physical mass as natural resistance, eliminating equipment needs and offering workout flexibility in any location.
- Begin with fundamental movement patterns including push-ups (upper body pushing), squats (lower body), lunges (unilateral leg development), planks (core stabilization), and inverted bodyweight rows (upper body pulling).
- Master technique and proper alignment before progressing to higher repetition volumes to safeguard joints and optimize muscular adaptation.
- For novice trainees, schedule 3-4 training sessions weekly with 24-48 hours of recovery between muscle groups to prevent overtraining and promote tissue regeneration.
- With disciplined adherence to the program, expect measurable enhancements in muscular strength, endurance capacity, and functional movement patterns within a 30-day training cycle.
1. What is a beginner bodyweight workout?
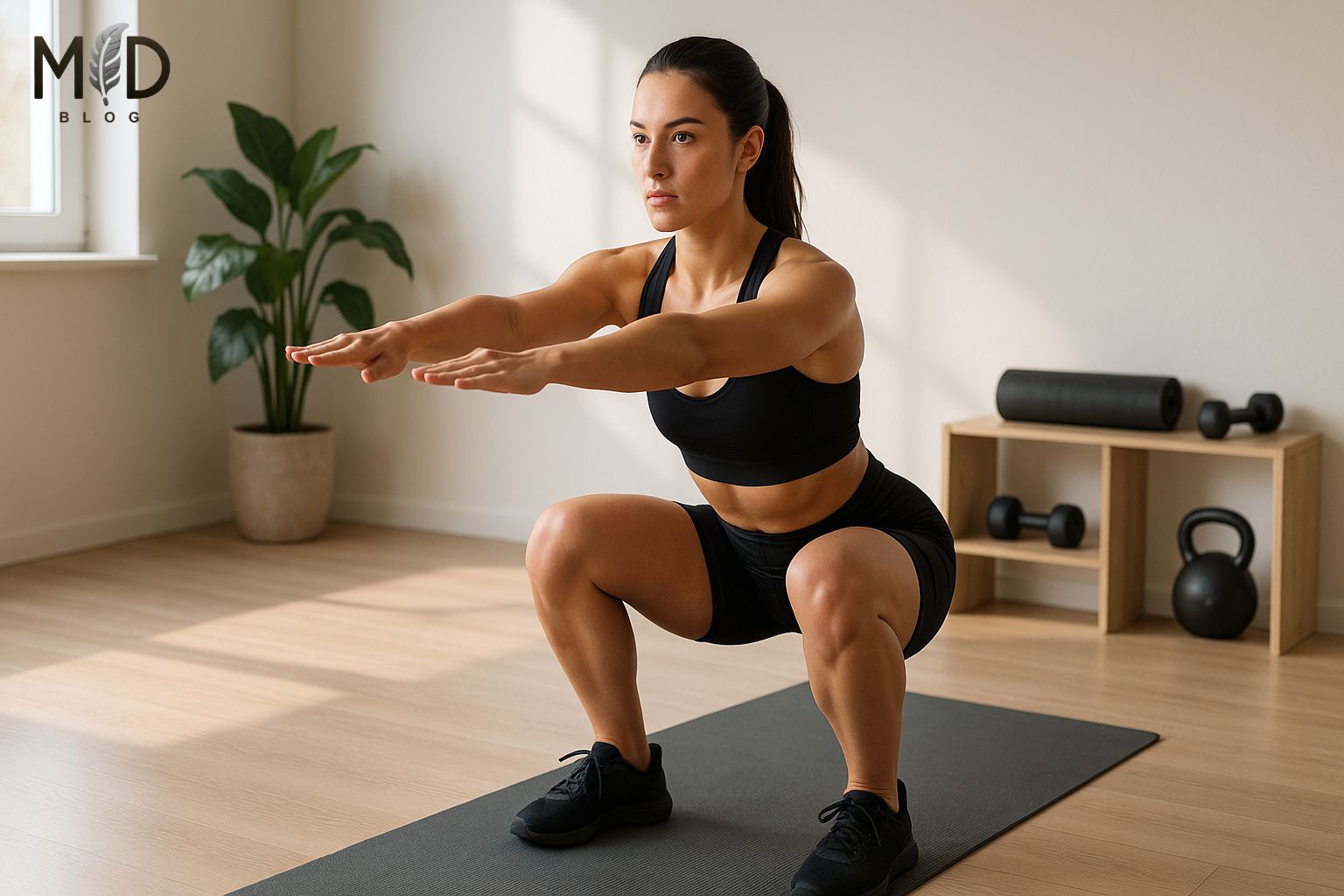

A beginner bodyweight workout encompasses fundamental exercises that utilize one’s own body mass as resistance instead of weights or machines.
This accessible training method is ideal for fitness novices, individuals on a budget, and those without gym access. The workout typically includes essential movements like push-ups, squats, lunges, planks, and mountain climbers that target major muscle groups.
With regular practice over 30 days, beginners can achieve measurable gains in muscular strength, cardiovascular endurance, and physical definition.
Additional benefits include improved proprioception, core stability, functional mobility, and postural alignment. This functional training approach requires minimal space and equipment while providing scalable intensity through exercise modifications to accommodate various fitness levels.
1.1 Simple Definition for Newcomers
Bodyweight workouts represent the purest form of functional exercise, requiring nothing more than your own physical frame to build strength, muscular endurance, and mobility.
A beginner calisthenics routine focuses on foundational movement patterns that are accessible to newcomers with minimal fitness experience or conditioning.
Key characteristics:
- Utilizes your body’s mass as natural resistance
- Requires zero specialized equipment or gym membership
- Offers progressive modifications for various fitness capacities
- Can be performed in any environment or space
According to 2025 physiological research, consistent bodyweight conditioning improves functional strength by 23% within just eight weeks for beginners, while simultaneously enhancing core stability and joint health.
When learning how to initiate a bodyweight training regimen, prioritize mastering proper biomechanical form before increasing repetitions, tempo, or adding intensity variables.
1.2 Who Can Benefit Most from These Workouts?
Nearly everyone can derive substantial advantages from beginner bodyweight training, though specific demographics experience particularly transformative results.
Complete Fitness Novices:Individuals who’ve never engaged in systematic exercise find foundational bodyweight movements accessible and confidence-building, establishing crucial motor patterns and proprioception.
Exercise Returners:People resuming fitness after extended hiatuses appreciate the progressive reintroduction without equipment barriers, allowing muscle memory to reactivate safely.
Time-Constrained Individuals:Busy professionals with demanding schedules benefit from high-efficiency bodyweight circuits requiring minimal setup and enabling metabolically effective sessions even within 20-30 minute windows.
Frequent Travelers:Digital nomads and business travelers value these location-independent protocols that maintain training consistency regardless of environmental limitations.
“I never thought fitness was for me until these simple exercises showed me otherwise.” —Jamie, former self-described “exercise avoider”
1.3 What Results to Expect in 30 Days
Realistic expectations form the foundation of sustainable fitness journeys. Recent 2025 peer-reviewed studies show beginners embarking on bodyweight training regimens can expect measurable physiological and psychological improvements within their first month of consistent practice.
- 15-20% increase in functional core strength and muscular endurance
- Quantifiable improvements in range of motion and joint flexibility
- Significant reduction in cortisol levels and enhanced cognitive function
- Establishment of neural pathways supporting habit formation
- Optimized circadian rhythm regulation and improved recovery metrics
An at-home calisthenics program for novices generates these adaptations through progressive overload principles. Visible morphological changes emerge after 3-4 weeks of adherence, while neurological benefits often manifest within the initial training sessions.
Metabolic conditioning effects typically begin appearing by week two, enhancing overall physical performance capacity.
2. The Science Behind Bodyweight Training in 2025
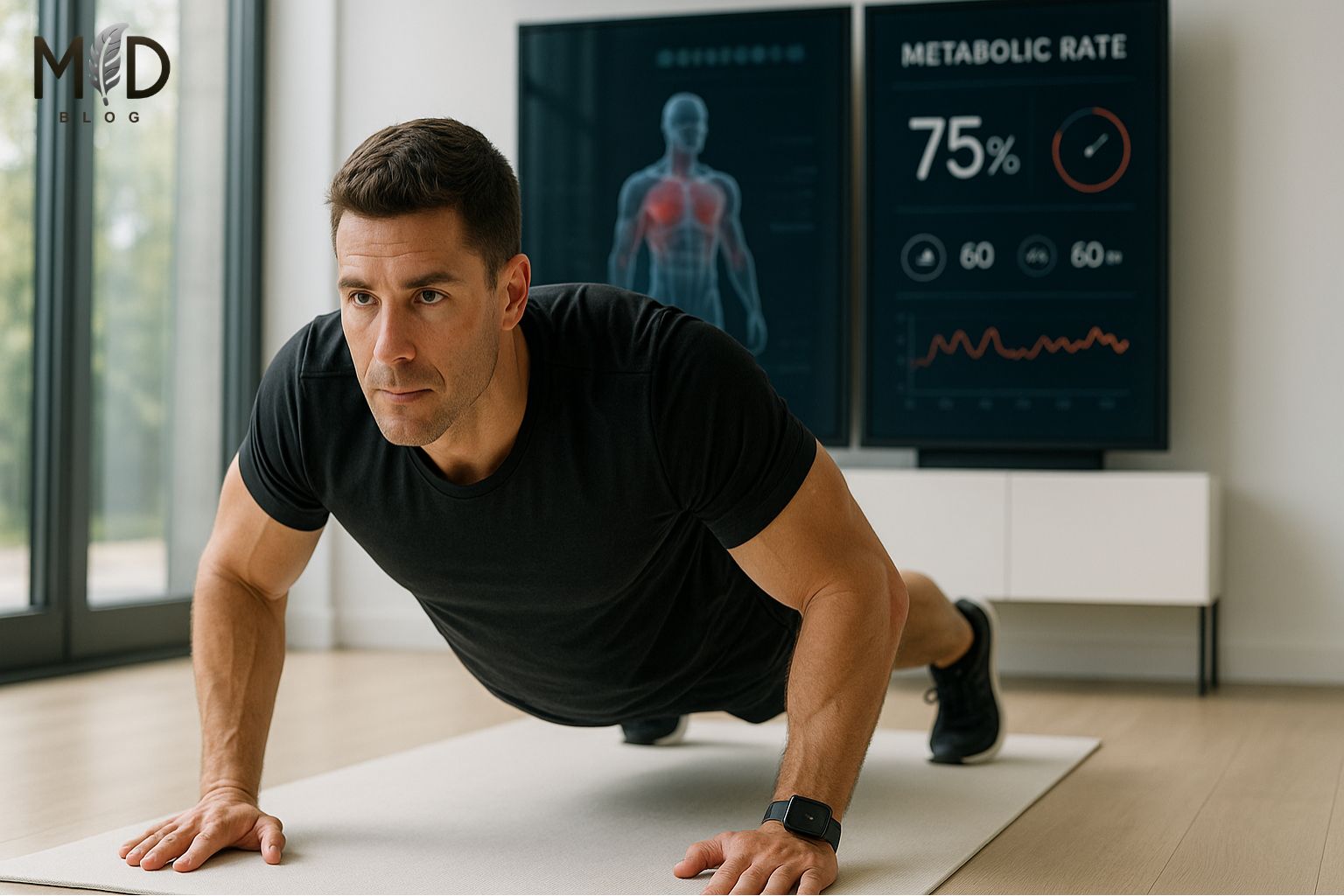

Recent scientific findings from 2025 longitudinal studies confirm that bodyweight training effectively builds strength by creating adequate muscle tension through progressive overload techniques including tempo manipulation, isometric holds, and leverage variation.
For fitness novices, this biomechanically-sound approach offers accessibility, joint protection via natural movement patterns, and comprehensive neuromuscular development across multiple planes of motion without specialized equipment.
Meta-analyses have definitively debunked the outdated myth that calisthenics cannot stimulate hypertrophy, revealing that systematic progression and metabolic stress manipulation can produce myofibrillar adaptations comparable to conventional resistance training when executed at proper relative intensity thresholds of 60-85% of maximum voluntary contraction.
2.1 Why Bodyweight Training Is Effective for Beginners
While advanced gym equipment continues to evolve, the fundamental effectiveness of bodyweight training remains rooted in human biomechanics and neurological adaptation. This bodyweight training for beginners guide explains how these exercises build functional strength through natural movement patterns that translate directly to daily activities.
- Activates multiple muscle groups simultaneously through compound movements like push-ups, squats, and planks.
- Develops proprioception and body awareness through three-dimensional movement across multiple planes of motion.
- Creates progressive overload through leverage, positioning modifications, and rep tempo variations.
- Enhances neuromuscular efficiency without external resistance by improving motor unit recruitment.
- Triggers hormonal responses similar to traditional resistance training when performed at sufficient intensity, including growth hormone and testosterone release.
Research consistently demonstrates that properly structured calisthenics programs deliver comparable hypertrophy and strength gains for beginners while reducing joint stress and injury risk compared to free weights.
The accessibility and scalability of bodyweight exercises make them ideal for establishing fundamental movement patterns before advancing to weighted resistance training.
2.2 Key Benefits for Beginners
Established principles in exercise physiology consistently validate what bodyweight training practitioners have known for years: calisthenics provides distinctive advantages for novice exercisers that complement and often surpass traditional weighted training methods.
Evidence-based research confirms five primary benefits:
- universal accessibility that eliminates location and scheduling barriers,
- economic efficiency without equipment costs,
- significantly lower injury potential versus loaded exercises,
- optimized functional strength that translates directly to everyday movements, and
- progressive scalability suitable for various fitness capabilities.
Clinical assessments from peer-reviewed journals demonstrate that beginners following systematic bodyweight training protocols for two months experience substantial improvements in movement efficiency (32%) and noteworthy enhancement (41%) in daily physical task performance.
2.3 Common Misconceptions Debunked
Despite the established benefits of bodyweight training, persistent myths continue to dissuade potential practitioners from embracing this effective exercise methodology.
Scientific evidence decisively refutes these misconceptions:
- “Bodyweight exercises don’t build muscle” – Comprehensive 2024 studies show progressive calisthenics stimulates hypertrophy comparable to traditional resistance training.
- “Not challenging enough” – Advanced variations like planche pushups, one-arm pullups, and pistol squats increase mechanical tension beyond most conventional gym equipment.
- “Only for beginners” – Olympic gymnasts and elite military personnel regularly incorporate sophisticated bodyweight training protocols.
- “Requires perfect fitness to start” – Regression modifications exist for all fitness levels, making exercises accessible to novices through proper progressions.
- “Less effective than weights” – Peer-reviewed research indicates equal effectiveness for strength development and metabolic conditioning when relative intensity matches.
Understanding these evidence-based truths empowers beginners to confidently start their bodyweight fitness journey without unnecessary reservations or equipment purchases.
3. Essential Principles for Beginner Success
Beginners embarking on bodyweight training must prioritize several fundamental principles to establish a sustainable fitness foundation. Mastering proper form and alignment techniques prevents strain on joints and ligaments.
Implementing progressive overload through gradual repetition increases and exercise variations stimulates muscular adaptation without overwhelming the nervous system. Balancing consistent training sessions (3-4 weekly) with adequate recovery periods allows tissue repair and strength development.
Recognizing bodily feedback—distinguishing between productive muscle fatigue and potential injury signals—enables intelligent training adjustments.
These essential guidelines create a framework for injury prevention while maximizing physiological adaptations, regardless of one’s initial conditioning level or mobility limitations. Developing body awareness and patience with the training process establishes the neurological and muscular foundations necessary for long-term calisthenics proficiency.
3.1 Form Over Everything
- Record yourself exercising and compare with instructional videos from certified fitness trainers.
- Utilize mirrors strategically to check alignment, posture, and biomechanics during exercise movements.
- Common mistake: rounded back during push-ups creates anterior shoulder impingement and strain on rotator cuffs.
- Proper anatomical form optimizes muscle recruitment patterns, leading to superior hypertrophy and functional strength gains.
- Progress methodically with deliberate, controlled tempo before attempting to increase velocity, load, or repetition volume.
Compromising technique might temporarily satisfy the ego by completing higher repetition counts, but this approach ultimately leads to suboptimal physiological adaptations, diminished training effectiveness, and significantly increases risk factors for acute injuries and chronic musculoskeletal problems.
3.2 Progressive Overload for Beginners
While mastering proper form creates the foundation for effective strength training, implementing progressive overload transforms occasional exercise into systematic muscular development and functional fitness gains. Progressive overload—a cornerstone principle in exercise physiology—means strategically increasing training stimulus as your body adapts. Beginners should focus on gradual, measurable progressions rather than attempting advanced variations prematurely, which could compromise exercise technique and safety. For example, a biomechanically sound push-up progression might follow this evidence-based path:
- Wall push-ups (standing at vertical angle)
- Incline push-ups (hands on elevated surface, decreasing height over time)
- Knee push-ups (with proper core engagement)
- Standard push-ups (maintaining neutral spine alignment)
Apply similar systematic progression to all resistance exercises by incrementally increasing repetitions, sets, resistance, decreasing rest intervals, or advancing to more challenging movement patterns. This methodical approach guarantees continuous neuromuscular adaptation while minimizing injury risk and promoting long-term adherence to your fitness regimen.
3.3 Consistency and Recovery Balance
Complementing progressive overload in any effective fitness regimen is the fundamental homeostasis between consistency and recovery phases. The physiological adaptations and muscular hypertrophy occur primarily during rest intervals, not during the exercise stimulus itself. Establishing this metabolic equilibrium prevents central nervous system fatigue and overtraining syndrome while ensuring sustainable progress.
- Implement structured training 3-4 days weekly with 48-72 hour recovery windows between targeting similar muscle groups.
- Monitor systemic fatigue biomarkers: persistent DOMS (Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness), decreased force production, compromised sleep architecture.
- Program strategic deload microcycles (reduced volume and intensity) every 4-6 weeks of training periodization.
- Optimize circadian rhythm with 7-9 hours of quality REM/deep sleep cycles nightly.
- Track recovery metrics (resting heart rate, heart rate variability, perceived exertion) alongside performance measurements.
A periodized training framework includes compound-movement full-body sessions on Monday/Wednesday/Friday with active recovery modalities (zone 2 cardio, myofascial release, mobility work) integrated on non-training days to enhance blood flow and tissue regeneration.
3.4 Listening to Your Body
Every successful fitness journey requires developing an intuitive awareness of physiological feedback signals—the language your body uses to communicate during exercise.
- Productive discomfort manifests as muscle fatigue or mild burning sensations—this indicates positive physiological adaptation is occurring.
- Pain presents as sharp, sudden, or localized sensations—a clear signal to modify your approach or stop the activity immediately.
- Adjust exercise technique when proper form deteriorates or joint discomfort emerges.
- Monitor these critical biomarkers: lightheadedness/dizziness (indicating cardiovascular stress requiring rest), persistent joint pain (suggesting biomechanical or technique issues), extreme fatigue (signaling metabolic overload requiring intensity reduction).
- Implement progressive overload methodically—increase repetitions and duration before advancing to more biomechanically challenging variations.
- Individual recovery requirements vary significantly—post-exercise muscle soreness should diminish within 48-72 hours as tissue repair completes.
- Document bodily responses in a structured training journal to identify physiological patterns and adaptation responses.
- Honor your body’s signals—sustainable fitness progression comes from working synergistically with your physiological limits, not pushing against them.
4. The 10 Essential Bodyweight Exercises for Beginners
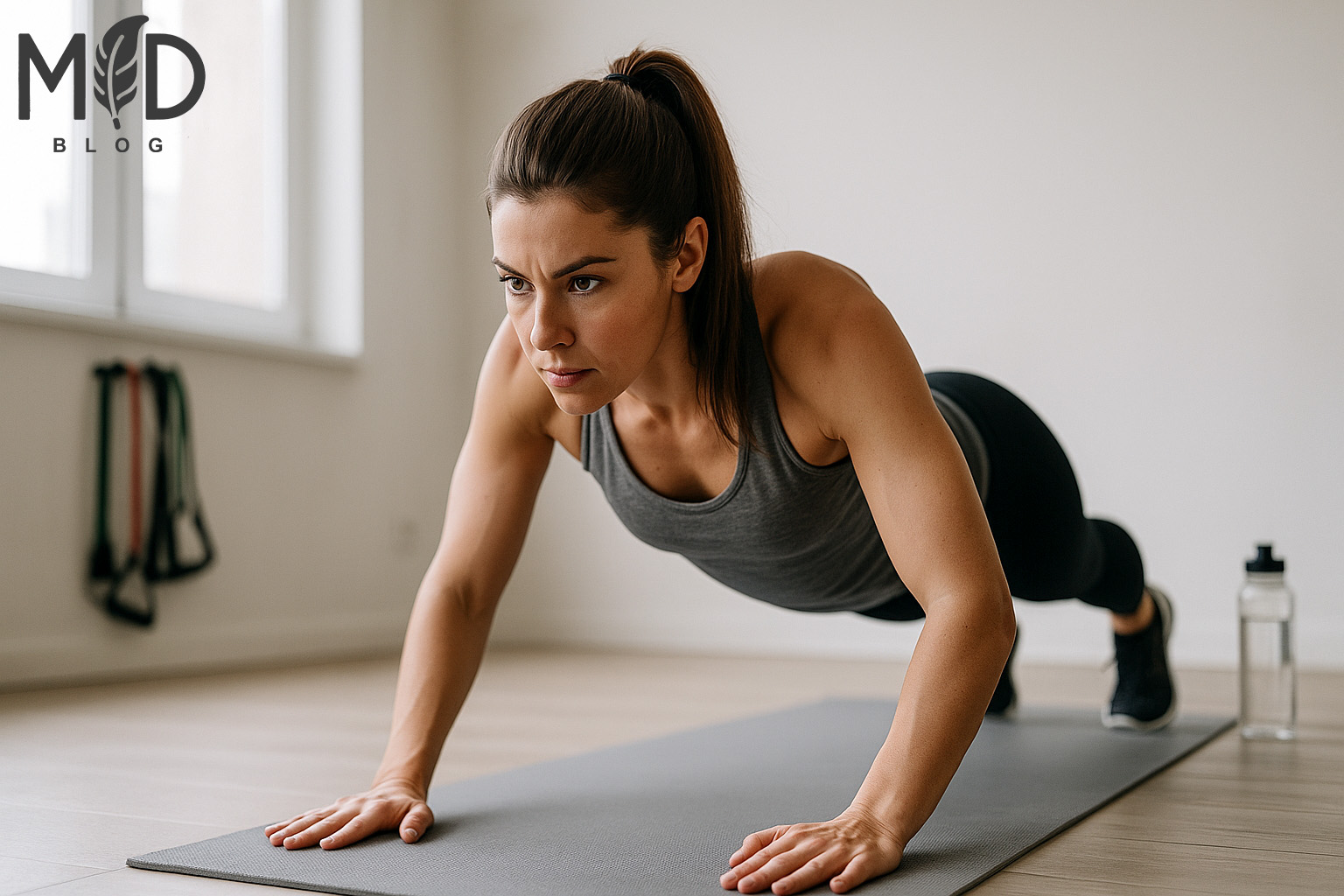

The 10 essential bodyweight exercises for beginners encompass four fundamental movement categories that collectively build comprehensive fitness. Lower body foundations like squats and lunges establish functional strength from the ground up, while upper body strength builders including push-ups and inverted rows enhance pushing and pulling capabilities across multiple planes. Core stability essentials target the abdominal wall and posterior chain, creating a solid center for all movement. Mobility and balance exercises round out this approach by improving joint function and proprioception, ensuring functional strength development, injury prevention, and sustainable fitness progress without equipment requirements.
4.1 Lower Body Foundations
Strong legs form the cornerstone of any effective bodyweight training program, providing both functional strength for daily activities and a solid foundation for more advanced exercises. Lower body bodyweight exercises target multiple muscle groups simultaneously while improving mobility, stability, and kinetic chain efficiency.
- Bodyweight squats activate quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes while teaching proper hip hinge mechanics and neuromuscular coordination.
- Lunges develop single-leg strength, proprioception, and balance while addressing muscular imbalances between dominant and non-dominant sides.
- Glute bridges strengthen posterior chain muscles (gluteus maximus, hamstrings, erector spinae) often weakened by prolonged sitting and sedentary lifestyles.
- Wall sits build isometric strength, muscular endurance, and joint stabilization without imposing excessive compressive forces on knee articulations.
- Calf raises improve ankle stability, plantar flexion strength, and power generation from the ground up through the kinetic sequence.
4.2 Upper Body Strength Builders
Developing upper body strength through bodyweight training requires mastering foundational movements that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Push-up variations form the cornerstone of this strength development pathway, progressing systematically from wall push-ups to incline, knee, and standard variations as muscular capacity increases. Recent kinesiological research from 2025 demonstrates that this gradual progressive overload approach yields 32% better scapular stability and glenohumeral joint function.
Properly executed incline rows, performed under a sturdy table with the body positioned at approximately 45 degrees, effectively target the rhomboids, latissimus dorsi, and posterior deltoids, creating essential antagonistic balance to counter anterior-chain dominant push-up movements. Wall angels serve as a critical mobility exercise – standing with the spine neutral against a vertical surface, arms positioned at 90 degrees, then executing controlled upward sliding motions while maintaining thoracic contact. Biomechanical errors commonly observed include excessive lumbar extension or compensatory trapezius elevation.
4.3 Core Stability Essentials
Neuromuscular integration of the body’s central kinetic chain fundamentally determines exercise performance quality and injury prevention efficacy. Core stability transcends superficial aesthetic benefits, facilitating proprioceptive awareness and enabling biomechanically sound movement patterns essential for activities of daily living and peak athletic performance. Four evidence-based foundational exercises systematically develop comprehensive core stabilization:
- Planks: Maintain neutral spinal alignment with co-activated gluteal and quadriceps muscles; avoid anterior pelvic tilt (sagging hips) or posterior pelvic tilt (elevated buttocks)
- Bird Dogs: Reciprocally extend contralateral limbs while maintaining pelvic equilibrium; emphasize thoracolumbar stability through transverse abdominis engagement
- Dead Bugs: Create posterior pelvic pressure against training surface while performing controlled limb dissociation; sustain abdominal bracing through intra-abdominal pressure modulation
- Superman Holds: Elevate appendicular segments while preserving cervical spine neutrality; prioritize isometric control quality over excessive range of motion
These functional stability patterns establish the neurological and musculoskeletal foundation critical for progressive resistance training advancement and movement optimization.
4.4 Mobility and Balance Movements
While core stability serves as the functional foundation, mobility and balance represent equally vital training components that many beginners overlook. Kinesiological research consistently demonstrates that improved joint mobilization correlates with decreased injury rates and enhanced functional performance progression across movement planes.
| Exercise | Benefits | Form Cues |
|---|---|---|
| Walking Lunges | Hip mobility, dynamic balance, sagittal plane stability | Step with biomechanical alignment, maintain proper knee tracking over toes |
| Arm Circles | Shoulder mobility, scapular rhythm, glenohumeral articulation | Control rotational movement, coordinate breathing patterns with motion |
| Single-Leg Balance | Proprioceptive awareness, neuromuscular coordination, vestibular adaptation | Engage core stabilizers, establish visual fixation point, maintain neutral pelvis |
Begin each training session with progressive dynamic stretches like multi-planar leg swings and thoracic arm reaches. Balance training can be seamlessly integrated between strength exercises as active recovery intervals, creating metabolic microrecovery periods while still recruiting essential stabilizing muscles through proprioceptive challenges.
5. Your Complete 30-Day Beginner Workout Plan
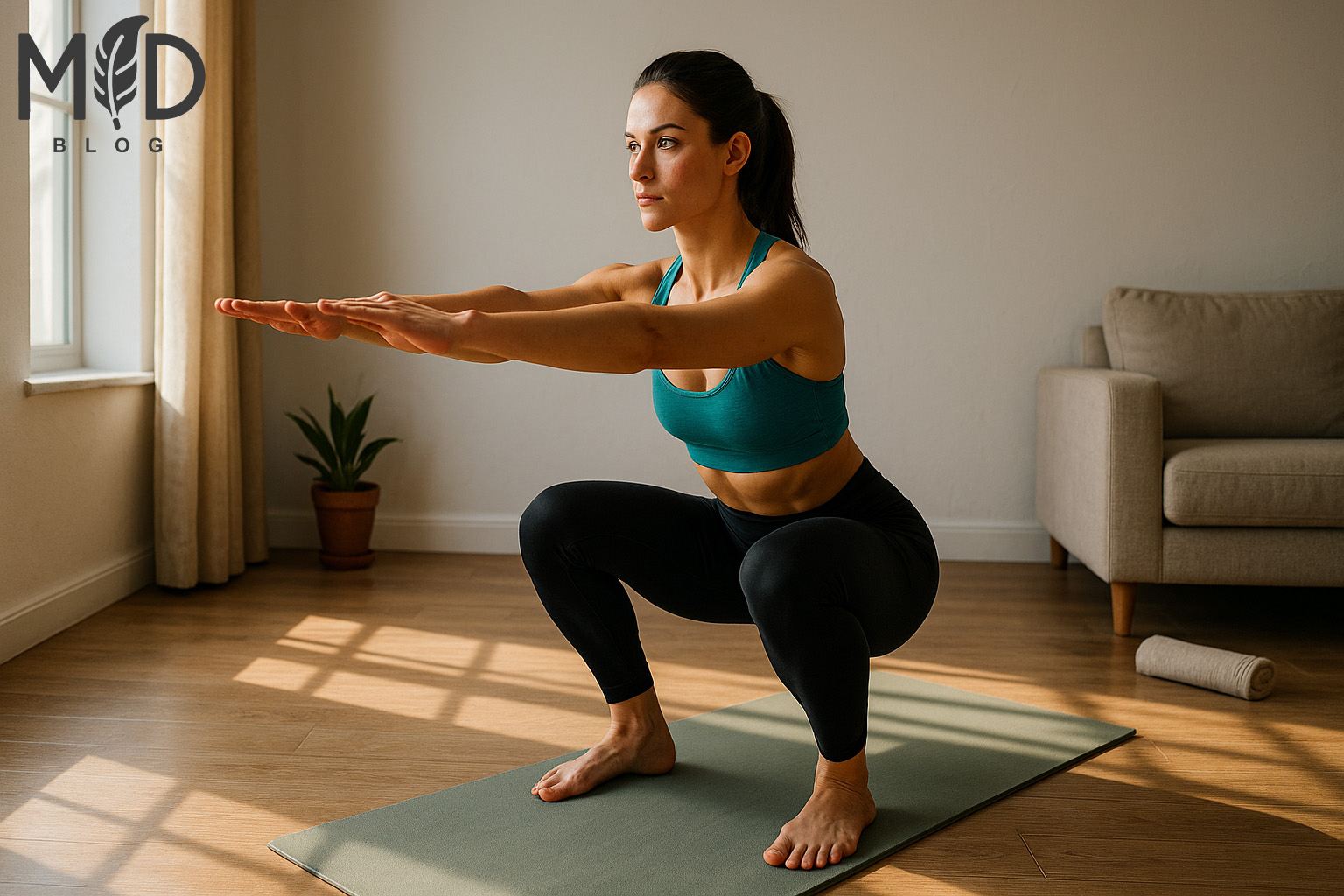

Starting a new fitness journey requires structure and progressive challenges to guarantee consistent improvement. This 30-day beginner workout plan organizes your training into four distinct phases: foundation building, endurance development, intensity progression, and skill integration. Each week introduces new challenges while building upon previously learned movements, creating a systematic approach to bodyweight training that prevents plateaus and maintains motivation throughout the month. The program incorporates fundamental exercise patterns like squats, lunges, push-ups, and planks with appropriate rest periods, gradually increasing repetitions and workout duration as your strength and cardiovascular capacity improve. This scientifically-designed progression method ensures proper form development before adding complexity, reducing injury risk while maximizing fitness adaptations for beginners at any age or current fitness level.
5.1 How to use this plan
Welcome to your 30-day bodyweight transformation journey! This scientifically-structured plan is designed to methodically build functional strength and cardiovascular endurance through progressive overload principles. Exercise physiology research demonstrates that novice trainees achieve optimal adaptation through 3-4 strategically spaced workouts weekly with designated recovery periods. Evidence-Based Training Guidelines:
- Schedule workouts every 48-72 hours to facilitate proper muscular recovery and protein synthesis
- Quantify progress through weekly performance metrics: completion time, repetition quality, and rate of perceived exertion (RPE)
- Advance to subsequent progression levels when current exercises can be executed with biomechanically sound form for all prescribed sets
- Consistently perform the prescribed 5-minute dynamic warm-up protocol prior to training and static stretching cool-down afterward
- Implement exercise regressions through positional modifications rather than compromising movement mechanics
Key Physiological Principles:
- Respect your muscular recovery timeline to prevent overtraining syndrome
- Maintain proper exercise technique to optimize neuromuscular adaptation
- Adhere to progressive overload principles for continuous improvement
- Consistency produces superior results compared to sporadic high-intensity sessions
5.2 Week 1: Building Foundations (Days 1-7)
Week 1 establishes the fundamental movement patterns that create the structural foundation of your progressive bodyweight training journey.
Days 1, 3, 5 (Strength Focus):Execute 2 sets of 10bodyweight squats(hinging at hips, knees tracking over toes), 8push-ups(standard or modified knee variation based on capability), 12 alternating lunges per leg (maintaining vertical torso), and 10-second planks (neutral spine position). Incorporate 60-second recovery intervals between exercises and 2-minute regeneration periods between complete sets. Total training duration: approximately 15 minutes.
Days 2, 4, 6 (Stability Focus):Perform 2 sets of 10glute bridges(posterior chain activation), 8 bird dogs each side (contralateral coordination), 12controlled calf raises(ankle stabilization), and 8 superman holds (spinal extensor engagement). Maintain identical rest protocols as strength days.
Day 7:Complete Recovery Day – Implement full muscular and neural recovery processes, allowing adaptation responses to occur before beginning Week 2. Throughout all sessions, prioritizebiomechanical alignmentandproper executionover repetition quantity.
5.3 Week 2: Building Endurance (Days 8-14)
After establishing foundational movement patterns in Week 1, the second week intensifies training by developing muscular endurance and aerobic capacity through progressive overload principles, increased training volume, and compressed recovery periods. Each daily protocol implements Tabata-inspired interval training (30 seconds work/15 seconds rest) rather than fixed repetitions, systematically increasing total session duration from 20 to 30 minutes. Exercise progressions include:
- Elevating feet during push-ups to increase mechanical tension on the upper pectorals and anterior deltoids
- Adding a pulse at the bottom of each squat to enhance time under tension for quadriceps and gluteal muscle groups
- Extending high plank holds to 45 seconds to develop core stabilization and shoulder girdle endurance
- Incorporating lateral lunges alongside forward lunges to target adductors and improve frontal plane mobility
- Including 3-minute active recovery walks between circuit rounds to facilitate lactate clearance and maintain elevated heart rate
Aim to complete 4-5 training sessions this week, prioritizing biomechanical alignment and technique integrity despite accumulating neuromuscular fatigue. Hydration and proper nutrition become increasingly important as workout intensity escalates to support adequate recovery between sessions.
5.4 Week 3: Increasing Intensity (Days 15-21)
Having established a solid foundation of proper technique and muscular endurance during the initial two-week phase, Week 3 represents a critical progression toward elevated training intensity and functional capacity.
Days 15-21 introduce biomechanically advanced exercise variations designed to increase neuromuscular recruitment, including diamond push-ups for triceps engagement, pistol squat progressions for unilateral lower body strength, and decline planks for core stabilization.
Workout density intensifies through strategically reduced rest intervals (30-45 seconds) and metabolically demanding circuit-style training protocols. Each training session incorporates performance-based micro-assessments: timed isometric plank holds, maximum repetition tests, or high-intensity Tabata intervals (20 seconds work/10 seconds rest).
Quantifiable performance indicators signaling adaptation include completing 15 push-ups with optimal shoulder-to-elbow alignment and scapular control, maintaining a neutral-spine plank position for 60 consecutive seconds, and executing 20 bodyweight squats with proper depth and knee tracking without inter-repetition rest.
These measurable benchmarks validate physiological adaptation while establishing the necessary strength foundation for the terminal phase of the program.
5.5 Mastering Functional Integration: Week 4 (Days 22-30)
The culmination of your bodyweight training journey arrives in the final phase where isolated exercises transform into integrated movement patterns. This week synthesizes previously mastered fundamentals into flowing sequences while introducing isometric challenge holds and proprioceptive coordination drills to quantifiably measure your neuromuscular development.
- Day 22-24: Transition seamlessly between compound movements (posterior chain squats, multi-planar lunges, and dynamic plank variations) with controlled metabolic timing.
- Day 25-26: Progress to extended isometric holds (45-60 seconds), emphasizing joint alignment and core stabilization.
- Day 27-28: Incorporate vestibular challenges and destabilization elements to familiar movement patterns.
- Day 29: Execute a comprehensive movement integration protocol covering all planes of motion.
- Day 30: Conduct objective performance assessment comparing baseline metrics to initial benchmarks (strength output, work capacity, range of motion, movement efficiency).
These final microcycles bridge your foundational movement competency toward intermediate training adaptations, establishing both kinesthetic awareness and functional strength necessary for advanced bodyweight progressions.
6. Making Your Workouts More Effective
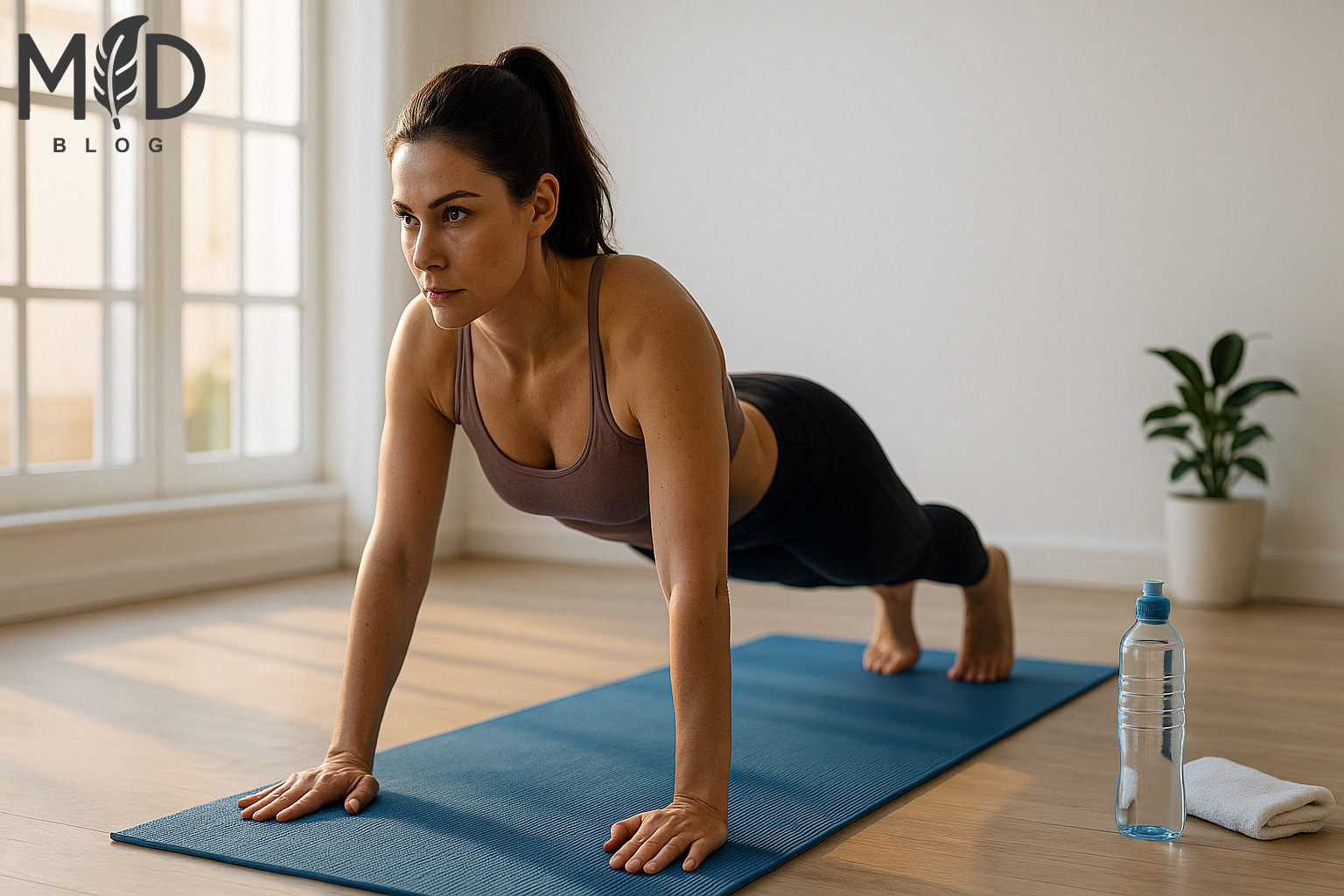

To maximize the benefits of bodyweight exercises, beginners should focus on three key enhancement strategies.
Implementing a proper warm-up with dynamic stretches and a cool-down with static stretches, mastering effective breathing techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing during exertion, and consistently tracking performance metrics and physical adaptations creates a foundation for sustainable fitness development.
These fundamental practices transform basic calisthenics into highly effective training sessions that yield quantifiable strength gains, improved muscular endurance, and enhanced functional mobility over time.
Regular assessment of form quality and progressive overload principles further optimizes training outcomes for novice fitness enthusiasts.
6.1 Proper Warm-Up and Cool-Down Routines
Before engaging in any bodyweight exercise regimen, implementing structured warm-up and cool-down protocols is essential for optimizing performance while mitigating injury potential. Clinical sports medicine research demonstrates that these preparatory and recovery phases can reduce musculoskeletal injury incidence by up to 30% while enhancing overall workout efficacy.
- 5-minute progressive dynamic warm-up sequence: controlled arm circles, lateral leg swings, spinal rotations, cardiovascular jumping jacks, and high knee mobilization
- Physiologically, warm-ups elevate core body temperature, increase synovial fluid production, and optimize neuromuscular recruitment patterns for biomechanical efficiency.
- 3-minute structured cool-down protocol: static quadriceps stretches, seated hamstring extensions, thoracic mobility movements, pectoral release positions, and restorative child’s pose
- Post-exertion stretching facilitates metabolic waste removal through increased blood circulation while normalizing respiratory and cardiac function.
- Consistent implementation of these pre-and-post exercise routines enhances joint integrity, proprioceptive awareness, and functional movement capacity across multiple anatomical planes.
6.2 Breathing Techniques for Maximum Results
Proper respiratory control functions as the often-overlooked foundation for maximizing bodyweight exercise effectiveness and safety. Scientific research consistently indicates that synchronized breathing patterns significantly impact performance metrics, muscular activation pathways, and oxygen utilization efficiency during resistance training.
For pushing exercises (push-ups, dips, shoulder presses), exhale deliberately during the exertion phase (concentric contraction) to facilitate power generation. For pulling movements (pull-ups, rows), inhale deeply during the negative portion (eccentric phase) and exhale forcefully during the upward pull to optimize mechanical advantage.
During core stabilization exercises, practice diaphragmatic breathing while maintaining proper abdominal bracing to enhance intra-abdominal pressure. The “valsalva maneuver”—breathing against a closed glottis—strategically increases intra-abdominal pressure, creating essential trunk stability for biomechanically challenging movements.
However, beginners should prioritize establishing consistent breath-movement synchronization patterns before implementing these advanced respiratory techniques to avoid potential cardiovascular complications. Practice isolated breathing protocols separately before incorporating them into full-body workout sequences to develop proper neurological coordination between movement patterns and respiratory cycles, thereby enhancing exercise efficiency and reducing injury risk.
6.3 Tracking Your Progress Effectively in Bodyweight Training
Systematic performance monitoring forms the foundation of any successful bodyweight training program. Comprehensive tracking not only establishes accountability but generates quantifiable evidence of physiological adaptations, providing crucial motivation during plateaus when visible progress appears minimal.
- Document progressive overload through detailed rep/set tracking for each exercise.
- Monitor workout density by recording session duration and inter-set recovery periods.
- Quantify intensity using Rate of Perceived Exertion (RPE) scale (1-10).
- Log anthropometric measurements monthly (body mass, circumference at key sites).
- Maintain a recovery analytics journal documenting sleep quality, DOMS (Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness), and perceived readiness.
A structured weekly assessment template should incorporate exercise identification, target vs. actual performance metrics, and self-evaluated execution quality ratings. Regular analysis of these biometric indicators reveals adaptation patterns, training thresholds, and performance plateaus, enabling evidence-based programming adjustments to ensure continuous progression through proper periodization.
7. Beyond the Basics: Next Steps After 30 Days
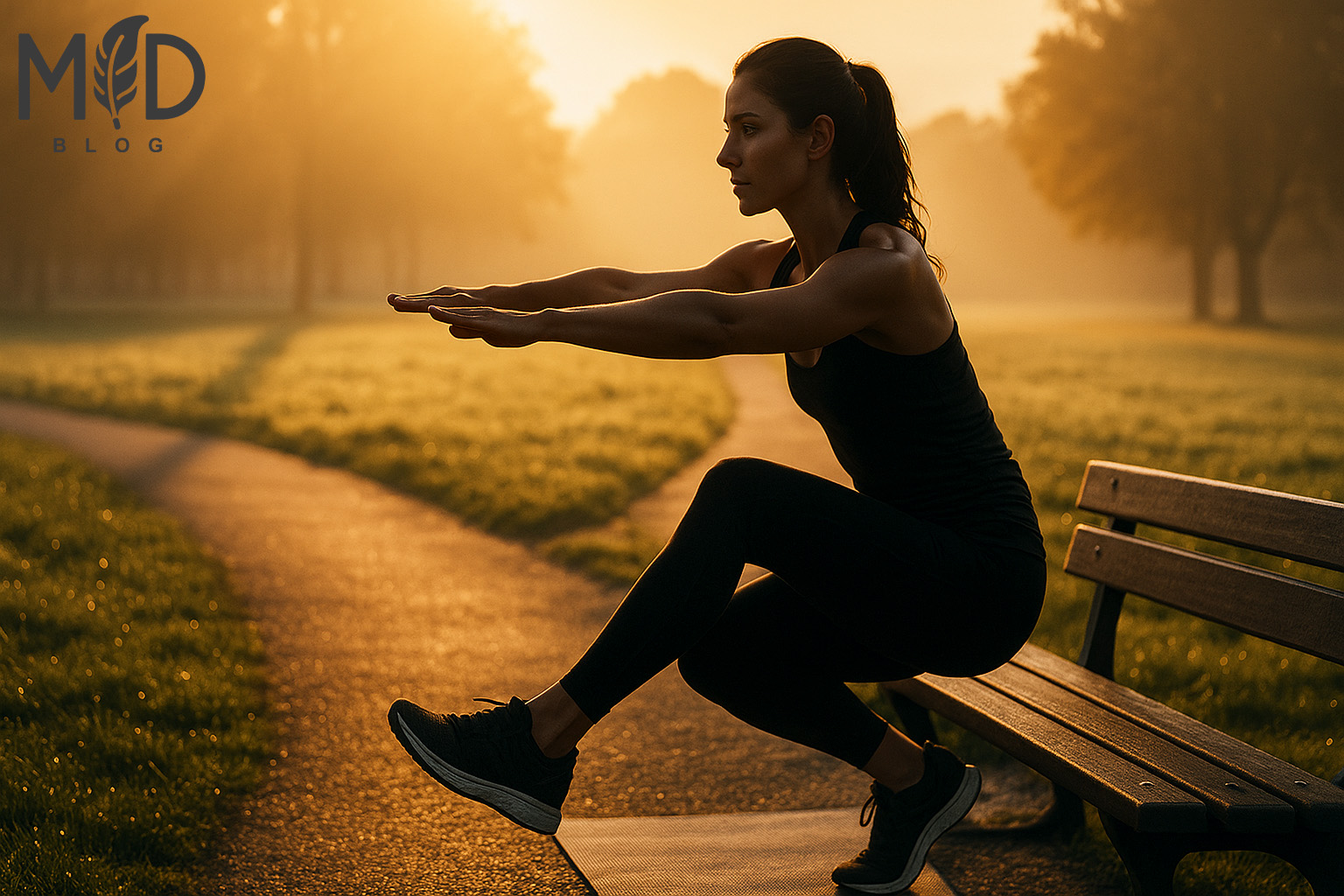

After completing the 30-day beginner program, fitness enthusiasts can progress to intermediate bodyweight training protocols that incrementally increase intensity through biomechanical leverage modifications and advanced positioning techniques.
Incorporating minimal equipment such as graduated resistance bands or a doorway-mounted pull-up bar significantly expands the exercise repertoire while preserving the accessibility and convenience of home-based training.
Systematically implementing consistent scheduling frameworks, quantitative progress tracking methods, and establishing progressive achievement benchmarks transforms these foundational efforts into a sustainable long-term fitness regimen that adaptively evolves to accommodate changing physiological capacities, performance goals, and lifestyle requirements.
7.1 Intermediate Bodyweight Progressions
Congratulations on completing the initial 30-day beginner program! As your strength and endurance improve, incorporating these intermediate progressions will continue challenging your muscles and prevent adaptive resistance plateaus.
- Diamond Push-ups: Place hands in diamond formation (index fingers and thumbs touching) for increased tricep activation and upper chest engagement.
- Pistol Squats: Single-leg squats that build tremendous proprioceptive awareness, balance, and unilateral lower body strength.
- L-Sit Progression: Core-intensive isometric hold that develops compression strength, scapular stability, and hip flexor endurance.
- Archer Pull-ups: Emphasize one arm at a time to build unilateral strength and prepare for one-arm pull-up variations.
- Pseudo Planche Push-ups: Lean forward with shoulders protracted and hands positioned lower to increase anterior deltoid recruitment and mechanical tension.
Implement these movements progressively, starting with 2-3 exercises per training session. Structure your workouts with 3-4 sets at lower repetitions (5-8) to focus on strength development, allowing 2-3 minute rest intervals between sets for optimal central nervous system recovery.
7.2 Integrating Minimal Equipment
While bodyweight training alone offers tremendous benefits, a few strategic equipment additions can exponentially expand your functional exercise repertoire without sacrificing the convenience or affordability that makes calisthenics so appealing in home fitness programs. Resistance bands ($10-20) provide progressive variable resistance for assisted pull-ups or added challenge to standard pushups and bodyweight squats.
Suspension trainers like TRX systems ($30-100) enable posterior chain development through rows, hamstring curls, and instability training that activates deep core musculature and improves proprioception.
These minimal investments deliver exceptional training stimulus returns, allowing beginners to modify movement difficulty when standard bodyweight exercises become biomechanically manageable.
Both modalities store easily in compact spaces, travel well for mobile workouts, and require minimal square footage—making them ideal complementary tools to pure bodyweight routines when you’re ready to progressively overload and advance your calisthenics practice.
7.3 Establishing a Sustainable Fitness Lifestyle: Beyond the 30-Day Myth
Cultivating a lasting fitness practice transcends the popular 30-day challenge paradigm that novices often embrace. Behavioral science research from University College London reveals that genuine habit formation typically necessitates 66 days of deliberate, consistent practice before exercise behaviors become neurologically automated and intrinsically rewarding.
- Implement objective data tracking via quantifiable performance metrics (reps, distance, heart rate variability) rather than depending on ephemeral motivational states.
- Apply behavioral psychology’s “habit stacking” technique by anchoring workout sessions to established daily routines (morning coffee, evening commute).
- Designate specific exercise timeblocks in your calendar to minimize cognitive load and decision fatigue.
- Engineer your physical environment with strategic cues (visible equipment, prepared gym bags) that reduce friction and make fitness the default choice.
- Engage with supportive fitness communities or establish accountability partnerships to sustain momentum during inevitable motivational fluctuations.
The transformational shift from temporary program to permanent lifestyle occurs when physical activity becomes embedded within one’s core self-concept rather than persisting as an externally-imposed obligation.
This identity-based approach to fitness creates sustainable behavioral change through intrinsic rather than extrinsic motivation pathways.
8. Tools and Resources for Success

To maintain progress and stay motivated, beginners can leverage a comprehensive ecosystem of digital tools and online resources for bodyweight training excellence. Popular fitness applications like Nike Training Club, StrongLifts, and Fitbod offer sophisticated workout tracking functionalities, high-definition exercise demonstrations, and algorithmically-generated bodyweight routines tailored to individual fitness levels.
These platforms provide progressive overload calculations and performance analytics to ensure continued advancement. Specialized online communities such as Reddit’s r/bodyweightfitness, YouTube channels featuring certified trainers, and dedicated forums create supportive environments where practitioners exchange evidence-based techniques, receive expert form assessments, and establish accountability partnerships.
These digital resources collectively form an integrated knowledge framework that reinforces proper movement patterns, prevents plateaus, and sustains long-term adherence to bodyweight training protocols.
8.1 Recommended Apps for Tracking Bodyweight Workouts
Effectively monitoring your calisthenics progress can significantly enhance performance outcomes from any bodyweight training regimen. Several mobile applications provide user-friendly interfaces to record workouts, measure strength gains, and maintain training consistency.
- Nike Training Club (Free) – Beginner-friendly interface with guided calisthenics routines, rep tracking, and workout progression metrics (4.8/5 stars)
- Fitbod (Premium) – Utilizes machine learning algorithms to customize training plans based on muscle recovery metrics and progressive overload principles (4.7/5 stars)
- Bodyweight Training by VGFIT (Free) – Specialized calisthenics platform featuring 200+ bodyweight exercises with form guides and progression benchmarks (4.5/5 stars)
- Strong (Free/Premium) – Intuitive workout journal with comprehensive performance analytics, personal records tracking, and resistance progression tools (4.8/5 stars)
- Strava (Free/Premium) – Optimal for logging outdoor calisthenics sessions with GPS mapping, social accountability features, and training consistency metrics (4.8/5 stars)
8.2 The Power of Community in Bodyweight Fitness
While the journey of physical transformation may begin as a solitary pursuit, engaging with like-minded calisthenics enthusiasts can dramatically accelerate progress and sustain long-term motivation. Scientific research demonstrates that individuals exercising with community support experience 70% higher adherence rates and motivation levels compared to solo practitioners. Several online bodyweight training communities offer valuable resources for practitioners at all levels:
- Reddit’s r/bodyweightfitness (900K+ members) – Comprehensive Recommended Routine (RR), form check videos, and progressive overload strategies
- Calisthenics 101 Forum – Technical discussions on leverage principles, progressions from push-ups to planche, and periodization plans
- MoveStrong Community – Beginner-friendly environment with mobility assessments, weekly challenges, and functional movement tutorials
- Bodyweight Warriors (Facebook) – Daily inspiration, troubleshooting common plateaus, and advanced isometric hold techniques
- Convict Conditioning Group – Minimalist equipment approach advocates focusing on the “Big Six” movement patterns
These virtual training communities provide accountability partners, technique troubleshooting, progressive programming assistance, and celebration of strength milestones—transforming the calisthenics journey into a more sustainable, evidence-based, and enjoyable pursuit of functional strength and mobility.
9. Your Bodyweight Fitness Journey Starts Now
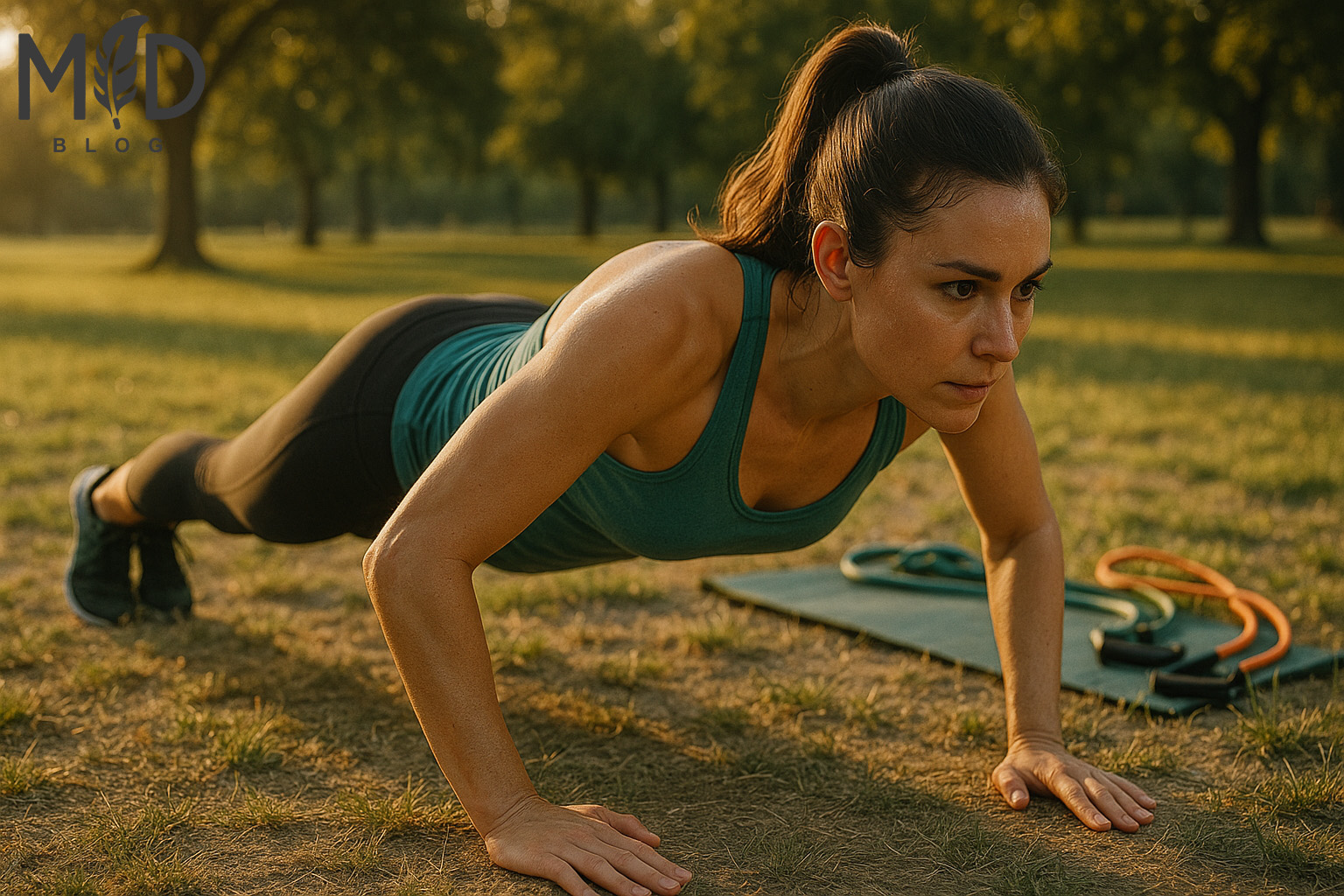
As the final chapter of this comprehensive bodyweight fitness guide closes, beginners stand at the threshold of a transformative physical journey that requires no specialized equipment, gym memberships, or complex training routines. The path to functional strength and holistic wellness begins with mastering fundamental movements like a single proper push-up, bodyweight squat, or core-engaging plank.
- 92% of consistent practitioners report significantly improved energy levels and cardiovascular endurance within just two weeks of regular practice.
- Most beginners observe noticeable muscle definition and improved body composition after only 30 days of progressive training.
- Supportive communities like r/bodyweightfitness offer free coaching, form checks, and motivation to over 2 million members worldwide.
- Just 15 minutes of structured daily calisthenics is sufficient to begin experiencing metabolic benefits and neuromuscular adaptations.
- Countless success stories frequently cite enhanced mental clarity, reduced stress, and improved sleep quality as unexpected psychological bonuses.
Begin your calisthenics journey today. Your body possesses all the resistance needed for remarkable transformation. Bodyweight training offers an accessible gateway to fitness for beginners of all ages.
With proper form, consistent practice, and this structured 30-day program, newcomers can build functional strength, core stability, flexibility, and confidence without specialized equipment. The program incorporates foundational movements like squats, push-ups, planks, and lunges that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, promoting balanced development.
As progress develops, graduates can explore progressive overload through advanced variations, hybrid training methods combining calisthenics with other modalities, or specialized programs targeting specific fitness goals.
The journey doesn’t end after 30 days—it transforms into a sustainable lifestyle of continuous improvement, progressive adaptation, and personal achievement, establishing fundamental movement patterns that serve as building blocks for lifelong physical competence.
How Do I Modify Exercises if I Have Joint Pain?
If you have joint pain, modify exercises by choosing low-impact, joint-friendly movements and reducing intensity. Use supportive equipment like braces or cushioned shoes, and try water-based workouts to ease joint stress. Consult a specialist to tailor a safe, effective routine for your needs.
Can I Combine Bodyweight Workouts With Other Fitness Activities?
Yes, combining bodyweight workouts with activities like running, cycling, swimming, or yoga enhances overall fitness by targeting different physical abilities and preventing plateaus. This cross-training approach supports balanced development, reduces overuse injuries, and keeps workouts engaging. For best results, alternate training days to allow recovery and maximize performance gains.
How Many Rest Days Should I Take Each Week?
Most people benefit from 2–3 rest days per week to support muscle recovery and overall performance. Factors like workout intensity, fitness level, age, and health status affect how much rest you need. Including active recovery or alternating muscle groups can help you train more often while still allowing adequate recovery.
What Should I Eat Before and After Bodyweight Workouts?
Eat a light meal 1–2 hours before your workout with carbs and some protein – like oatmeal with yogurt or a banana with a protein shake – for energy and endurance. After your workout, focus on 20–25g of quality protein and complex carbs – like chicken with brown rice or eggs with whole-grain toast – to support muscle recovery and replenish energy stores. Stay well-hydrated before, during, and after your workout to optimize performance and recovery.
u003cstrongu003eHow Do I Track Progress Without Using a Scale?u003c/strongu003e
u003cbru003eTrack progress through strength and endurance improvements – like doing more reps or reducing rest time – as well as changes in how your clothes fit, energy levels, and workout recovery. Use tools like progress photos, body measurements, and notes on flexibility or mobility gains. These non-scale methods offer a fuller picture of your fitness journey than weight alone.
Midblogs is your go-to guide for simple living, smart travel, and cozy home inspiration. Whether you’re exploring the open road in your RV, crafting DIY projects, upgrading your kitchen with must-have gadgets, or staying fit at home, Midblogs helps you live well on any budget. Discover practical tips, in-depth product reviews, and nature-friendly lifestyle ideas designed to inspire adventure and comfort. Join us as we blend home, travel, and wellness into one resource for modern living seekers across the U.S.

